
Table of Contents
Introduction
Leg training is often overlooked but is a fundamental component of a balanced and powerful physique. Not only do strong legs improve athletic performance and daily functionality, but they also contribute to overall strength, stability, and endurance. Whether you aim to build muscle, enhance strength, or boost endurance, training your legs is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the anatomy of the leg muscles, and their importance in overall fitness, and provide you with 12 effective exercises to train them. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and tools to design a leg workout that suits your goals.
Anatomy of the Leg Muscles
Before diving into the exercises, it’s essential to understand the anatomy of your legs. The major muscles of the legs can be divided into four key areas:
- Quadriceps (Front of the Thigh): This group consists of four muscles—rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. These muscles are responsible for extending the knee and are heavily involved in movements like squats and lunges.
- Hamstrings (Back of the Thigh): The hamstrings, made up of the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus, are crucial for knee flexion and hip extension. Exercises like deadlifts target these muscles.
- Glutes (Buttocks): The gluteal muscles (gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus) are some of the strongest in the body. They play a key role in hip extension, abduction, and external rotation. Movements such as hip thrusts and squats activate the glutes.
- Calves (Lower Leg): The calf muscles consist of the gastrocnemius and the soleus. These muscles are responsible for plantar flexion (pointing your toes) and are targeted through exercises like calf raises.
Understanding the functions of these muscles will help you train them more effectively, ensuring that your workouts are well-rounded and targeted.
Why Training Your Legs Is Crucial

Leg training offers many benefits beyond just aesthetics. Here’s why you should never skip leg day:
1. Strength and Power
Your legs contain some of the largest muscles in your body, which means they can generate significant strength and power. Training them with compound movements like squats and deadlifts boosts overall strength and helps improve performance in other exercises.
2. Improved Athletic Performance
Whether you’re a runner, cyclist, or play a sport, strong legs are essential for athletic performance. Your quads, hamstrings, and glutes provide the power needed for sprinting, jumping, and changing direction quickly.
3. Better Functional Mobility
Leg strength translates directly into better functional movement in everyday life. Activities like walking, climbing stairs, lifting objects, and even maintaining balance rely heavily on the strength and stability of your legs.
4. Increased Muscle Mass
The more muscle mass you have, the higher your resting metabolic rate. Leg exercises that target large muscle groups can help increase your overall muscle mass, making it easier to burn fat and maintain a lean physique.
5. Balanced Physique
Neglecting your legs leads to an unbalanced physique. Building strong legs helps create symmetry, improves posture, and enhances the appearance of your upper body by making you look more proportionate.
6. Injury Prevention
Strengthening the muscles around your knees, hips, and ankles helps protect your joints and reduces the risk of injuries, particularly during high-impact activities.
Now that you understand why leg training is so important, let’s dive into the exercises. We’ll cover 12 essential movements that target all areas of your legs, from quads and hamstrings to glutes and calves.
12 Effective Leg Exercises to Build Strength and Size
The following exercises are categorized by the muscle groups they target. A well-rounded leg workout should include a mix of compound and isolation movements to ensure you’re working every part of your legs.
Prior to embarking on your leg drill journey, it’s essential to dedicate 10 minutes to cardio; all the necessary information is available here.
1. Squats (Barbell or Bodyweight)

Target Muscles: Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings
The squat is the king of all leg exercises. It’s a compound movement that works almost every muscle in your lower body, including the quads, hamstrings, glutes, and even your core.
How to Perform:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Lower your hips back and down, as if sitting in a chair.
- Keep your chest up, back straight, and knees aligned with your toes.
- Push through your heels to return to the starting position.
Tips: For added intensity, perform barbell squats by placing a loaded barbell on your upper back. To protect your knees and back, avoid letting your knees collapse inward and keep your lower back neutral.
2. Deadlifts (Conventional or Romanian)

WARNING: To protect your back from injury, it’s crucial to either lift lighter weights or utilize a stomach belt for added support.
Target Muscles: Hamstrings, Glutes, Lower Back
Deadlifts are another powerhouse exercise for building lower body strength, focusing primarily on the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back.
How to Perform:
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart, with a barbell in front of you.
- Bend at the hips and knees, grasping the bar with an overhand grip.
- Lift the bar by extending your hips and knees, keeping your back flat.
- Lower the bar back down with control.
Tips: Romanian deadlifts (RDLs) place more emphasis on the hamstrings, while conventional deadlifts work the entire posterior chain. Keep the barbell close to your body throughout the lift.
3. Lunges (Walking or Stationary)
Target Muscles: Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings
Lunges are a unilateral exercise, meaning they work one leg at a time. This helps improve balance and corrects any muscle imbalances between your legs.
How to Perform:
- Stand tall with feet hip-width apart.
- Take a step forward with one leg, lowering your hips until both knees are bent at about 90 degrees.
- Push through your front heel to return to the starting position.
Tips: For an added challenge, try holding dumbbells in each hand or performing walking lunges to increase difficulty and endurance.
4. Leg Press
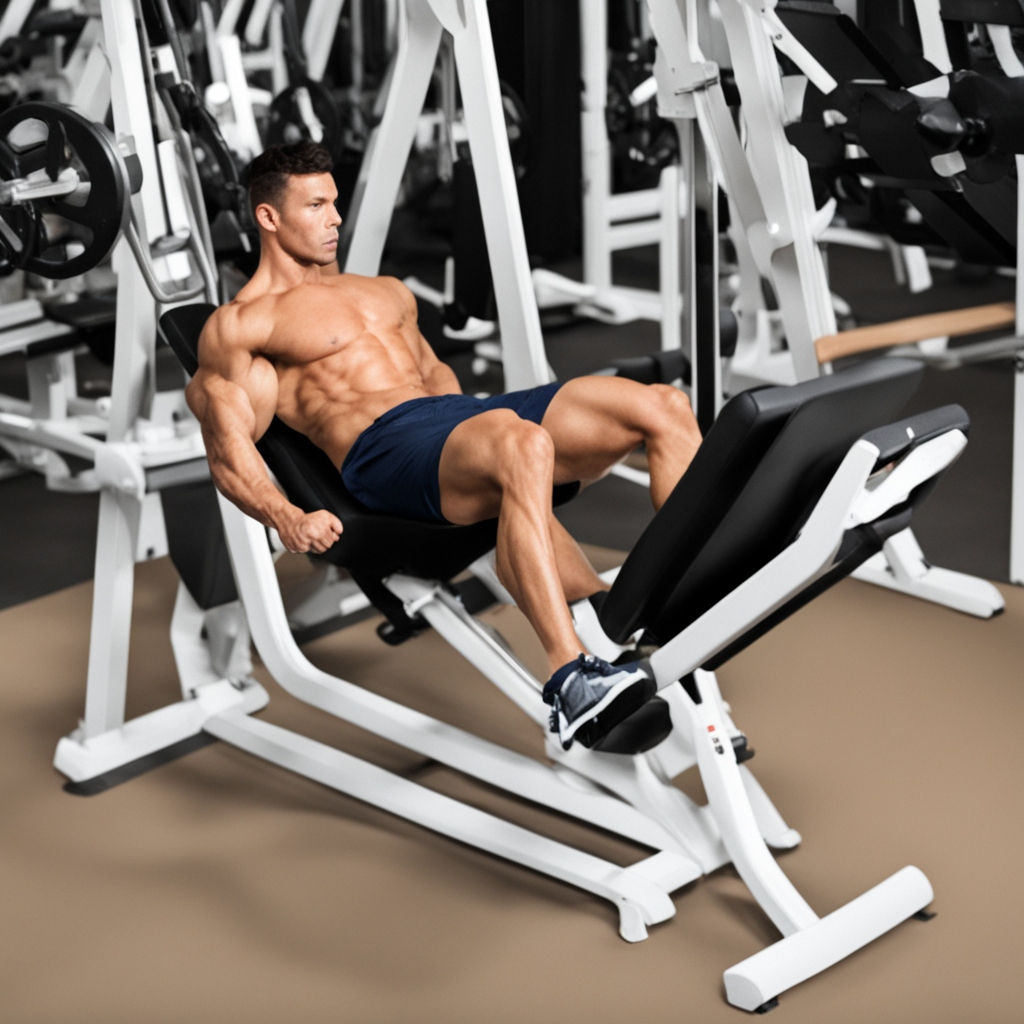

Target Muscles: Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings
The leg press machine is a great alternative to squats if you want to focus more on isolating your quads and glutes without putting as much strain on your lower back.
How to Perform:
- Sit on the machine with your feet on the platform, shoulder-width apart.
- Lower the platform by bending your knees, then push back up to the starting position.
Tips: Avoid locking out your knees at the top of the movement to keep tension on the muscles. You can adjust your foot placement on the platform to target different muscle groups.
5. Bulgarian Split Squats

Target Muscles: Quads, Glutes
This advanced variation of the lunge is an excellent exercise for building strength and stability in the legs. It’s especially effective for isolating the quads and glutes.
How to Perform:
- Stand a few feet in front of a bench, with one foot resting on the bench behind you.
- Lower your hips until your front knee is bent at 90 degrees.
- Push through your front heel to return to the starting position.
Tips: Keep your chest up and core engaged to maintain balance. Hold dumbbells for added resistance.
6. Glute Bridges (Hip Thrusts)
Target Muscles: Glutes, Hamstrings
Glute bridges or hip thrusts are among the best exercises for isolating and building your glutes.
How to Perform:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground.
- Push through your heels to lift your hips toward the ceiling, squeezing your glutes at the top.
- Lower your hips back down with control.
Tips: For more intensity, place a barbell across your hips or use a resistance band around your knees to increase glute activation.
7. Leg Extensions
Target Muscles: Quads
Leg extensions isolate the quadriceps, making them an excellent exercise for strengthening and building the front of your thighs.
How to Perform:
- Sit on the leg extension machine with your legs under the pad.
- Extend your legs until they are straight, then slowly lower back to the starting position.
Tips: Focus on controlling the movement, especially during the lowering phase, to maximize muscle tension.
8. Hamstring Curls
Target Muscles: Hamstrings
Hamstring curls are an isolation exercise that targets the back of the thighs. They can be done on either a lying or seated leg curl machine.
How to Perform:
- Lie face down on the machine with the pad resting against your lower legs.
- Curl your legs toward your glutes, then slowly lower them back down.
Tips: Keep your hips pressed against the bench and avoid using momentum to lift the weight. Focus on feeling the contraction in your hamstrings.
9. Step-Ups
Target Muscles: Quads, Glutes
Step-ups are a great functional exercise that mimics climbing stairs. They target your quads, glutes, and hamstrings while improving balance and coordination.
How to Perform:
- Stand in front of a bench or platform.
- Step onto the platform with one foot, pushing through your heel to lift your body.
- Lower yourself back down and repeat on the other leg.
Tips: Hold dumbbells for added resistance and ensure you’re stepping with control rather than jumping or using momentum. This will help maximize muscle engagement and reduce the risk of injury.
10. Calf Raises
Target Muscles: Calves (Gastrocnemius and Soleus)
Calf raises are a simple yet highly effective exercise for targeting the muscles of your lower legs. They can be performed standing or seated, with or without weights.
How to Perform (Standing Calf Raises):
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart, with your toes on the edge of a raised platform.
- Lower your heels below the platform, feeling a stretch in your calves.
- Push through the balls of your feet to raise your heels as high as possible, then lower back down with control.
How to Perform (Seated Calf Raises):
- Sit on a bench or calf raise machine with your feet flat on the platform.
- Place a weight on your knees or use the machine’s resistance.
- Raise your heels as high as possible, squeezing your calves at the top, then lower them back down.
Tips: Focus on the full range of motion to fully engage the calf muscles. For standing calf raises, you can adjust your foot position (toes in, out, or neutral) to target different parts of the calf.
11. Sumo Squats
Target Muscles: Inner Thighs, Glutes, Quads
Sumo squats are a variation of the traditional squat that targets the inner thighs (adductors) and glutes more intensely due to the wider stance.
How to Perform:
- Stand with your feet wider than shoulder-width apart, toes pointed slightly outward.
- Lower your hips down and back, keeping your chest up and knees tracking over your toes.
- Push through your heels to return to the starting position.
Tips: Keep your back straight and avoid leaning forward. Holding a dumbbell or kettlebell in front of your chest (goblet style) can add resistance and help with balance.
12. Box Jumps
Target Muscles: Quads, Glutes, Calves
Box jumps are a plyometric exercise that not only builds strength but also improves explosive power and cardiovascular fitness.
How to Perform:
- Stand in front of a sturdy box or platform.
- Bend your knees slightly, then explode upwards, jumping onto the box.
- Land softly on the box with both feet, then step back down and repeat.
Tips: Focus on a soft, controlled landing to minimize the impact on your joints. Start with a lower box height and gradually increase as you build confidence and strength.
Structuring Your Leg Workout
With these 12 exercises in your arsenal, you can structure a well-rounded leg workout that targets all the major muscle groups in your lower body. Here’s how you can put together a leg workout routine based on your goals:
1. Strength and Power Focus
If your primary goal is to build strength and power, your workout should emphasize heavy compound lifts with lower repetitions and longer rest periods.
Sample Workout:
- Barbell Squats: 4 sets of 5 reps
- Deadlifts: 4 sets of 5 reps
- Bulgarian Split Squats: 3 sets of 8-10 reps (each leg)
- Leg Press: 3 sets of 8-10 reps
- Calf Raises: 4 sets of 12-15 reps
Rest: 2-3 minutes between sets for squats and deadlifts, 1-2 minutes for other exercises.
2. Hypertrophy (Muscle Growth) Focus
To maximize muscle growth, you’ll want to use a moderate weight with higher repetitions and shorter rest periods to keep the muscles under tension for longer.
Sample Workout:
- Leg Press: 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Romanian Deadlifts: 4 sets of 10-12 reps
- Lunges: 3 sets of 12-15 reps (each leg)
- Leg Extensions: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Hamstring Curls: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Calf Raises: 4 sets of 15-20 reps
Rest: 60-90 seconds between sets.
3. Endurance and Conditioning Focus
Your workouts should incorporate higher repetitions, lighter weights, and shorter rest periods for endurance and conditioning. You can also include plyometric exercises like box jumps to enhance cardiovascular fitness.
Sample Workout:
- Bodyweight Squats: 3 sets of 20-25 reps
- Walking Lunges: 3 sets of 15-20 reps (each leg)
- Step-Ups: 3 sets of 15-20 reps (each leg)
- Glute Bridges: 3 sets of 20 reps
- Box Jumps: 3 sets of 15 reps
- Standing Calf Raises: 4 sets of 20-25 reps
Rest: 30-60 seconds between sets.



[…] https://samuellancite.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-traini-legs-12-best-drills/Muscles Worked: Quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, calves. […]